
European Academies Science Advisory Council (EASAC) vaccination information campaign
Recently, media reported that the progress of vaccination programmes to fight the COVID-19 pandemic is slowing down in many European countries because of a lack of demand. In other world regions, it is the supply rather than the demand that is causing delays. Because of EASAC’s contact with the national science academies of Africa, Asia and the Americas, the European network of academies are acutely aware of the discrepancy in global vaccination efforts.
In order to provide information about COVID-19 vaccines to the European public, a number of eminent experts nominated by EASAC member academies have given answers to some of the most pressing questions, in short video interviews.
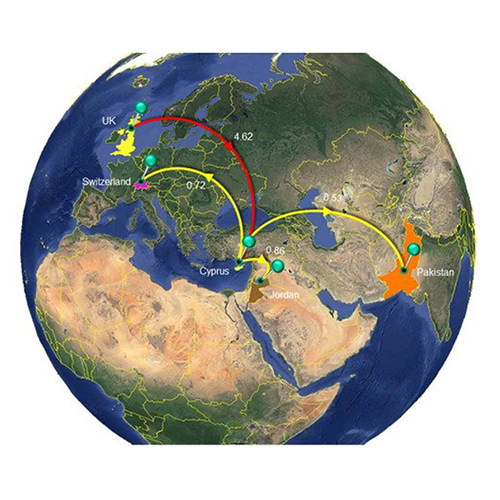
A Comprehensive Molecular Epidemiological Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Cyprus from April 2020 to January 2021: Evidence of a Highly Polyphyletic and Evolving Epidemic
We are pleased to announce that our article “A Comprehensive Molecular Epidemiological Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Cyprus from April 2020 to January 2021: Evidence of a Highly Polyphyletic and Evolving Epidemic” (Viruses 2021, 13, 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061098 ) was published in Viruses on June 9, 2021.

Research and Innovation Foundation, Cyprus
Distinguished Researcher 2020 Award in Life Sciences
December 2020
Timestamps on video:
1:05:19-1:07:19 Presentation of Professor Leontios G. Kostrikis
1:11:27-1:14:49 Acceptance speech
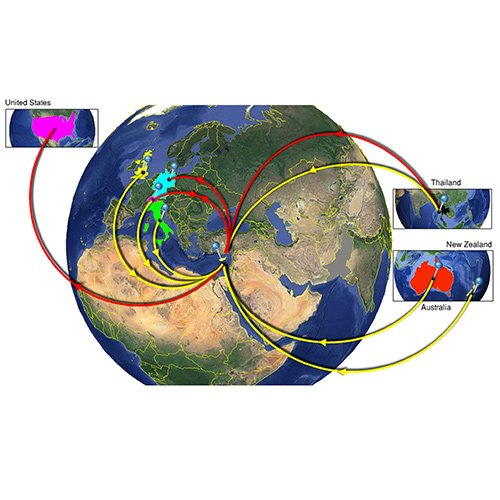
HCV Phylogeny of the General Population and High-Risk Groups in Cyprus Identifies the Island as a Global Sink for and Source of Infection
We are pleased to announce that our article 10.1038/s41598-019-46552-7 “HCV Phylogeography of the General Population and High-Risk Groups in Cyprus Identifies the Island as a Global Sink for and Source of Infection” (SREP-19-11797) was published in Nature Scientific Reports on July 11, 2019.